
“Interventions for children and adolescents with stuttering”
“Interventions for children and adolescents who stutter”
Intervention or treatment programs rely on research findings. It helps to follow the best practices available for a given disease or disorder. Here’s a peek into some research based on ‘Stuttering’:
Researchers and authors Amanda Brignell , Michelle Krahe, Martin Downes , Elaina Kefalianos , Sheena Reilly , Angela Morgan conducted research on Stuttering. They published their research in the Journal of Fluency Disorders in 2021.
Read the original article at click here
Let’s find out more about their research findings …
What was the purpose of the study?
- This study critically analyses the evidence for the effectiveness of treatment(s) for children and adolescents who stutter.
What is stuttering?
- Stuttering is a speech disorder. It is characterized by involuntary repetition or prolongation of sounds, syllables, or words. It can also include involuntary hesitation or pauses that disrupt the rhythmic flow of speech (World Health Organisation, 2001).
Why is the treatment of stuttering important?
- Evidence suggests later psychological difficulties may arise during the school years in children who stutter
- Many believe that school-aged children who stutter are at increased risk of teasing, bullying, and anxiety. Stuttering is also highly associated with occupational and educational under-achievement and suicidal thoughts.
- If not treated during childhood, persistent stuttering can result in lifelong social, educational, and occupational reduced quality of life.
- A higher proportion of adults who stutter have social phobia and anxiety compared to adults who do not stutter.
How did the authors conduct this research?
The authors searched for different types of research articles published on stuttering. A total of nine databases and three clinical trial registries were the source of information. The authors studied the articles for more specific details.
The researchers collected data on the following: authors, year, country, study design, and study aim. They also made a note of details of the intervention (key features), and comparator/control. In addition, the authors complied details of participants (age, gender, and inclusion/exclusion criteria), study measures, outcomes (time points, primary and secondary outcomes and main outcomes) and funding sources.
What was studied from the collected articles?
The authors looked at stuttering severity from the shortlisted studies. They provide an overview of the research evidence through summaries of the study characteristics, outcomes measured, and key findings.
What were the results of the study?
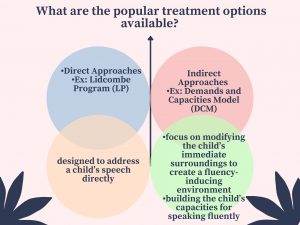
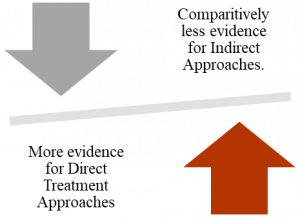
Evidence for Direct versus Indirect Approaches for Stuttering Intervention:
A drop in the percentage of stuttering was common across all studies included in the research. It was true in the case of both direct approach and indirect approaches. Lidcombe Program, a direct approach to the treatment of stuttering, was the most effective for children aged less than 6 years.
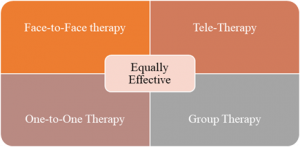 The authors studied therapy delivered in various formats. One-to-one or group therapy through various modes such as face-to-face or tele-mode was studied. They found all types of service delivery modalities to be equally effective. Also, the severity of stuttering reduced at almost the same time across all shortlisted studies.
The authors studied therapy delivered in various formats. One-to-one or group therapy through various modes such as face-to-face or tele-mode was studied. They found all types of service delivery modalities to be equally effective. Also, the severity of stuttering reduced at almost the same time across all shortlisted studies.
- “Interventions for children and adolescents with stuttering” - April 7, 2023
- What is Speech Therapy and its effect? - December 21, 2022
- Dysphagic disorder in a cohort of COVID-19 patients - December 13, 2022

Leave a Comment
(1 Comment)
Thank you for the information in this post.
Categories
Recent Posts